Pediatric Orthopedics
Overview
Our caring team of pediatric orthopedicians, nurses and technicians tend to the unique needs of congenital, developmental and acquired musculoskeletal (bones, joints and related soft tissues – muscles, tendons, ligaments) disorders in children of all ages.
What is Pediatric Orthopedics?
Pediatric Orthopedics deals with treating broken bones, congenital deformities and unexplainable injuries in children. When children have conditions that restricts their ability to move, their discomfort differs from that of an adult. They may not be able to accurately express their pain.
Whether it is a bone fracture while playing basketball or a clumsy fall, the severity of which was underestimated, children are more likely to face orthopedic concerns as they grow older.
When should you visit a pediatric orthopedician?
If your child complains of bone, joint or muscle pain beyond traditional growing pains or suffers from an acute injury, it is time to visit a pediatric orthopedician.
Sitaram Bhartia Hospital takes a multidisciplinary approach to integrate all medical, social and psychological and developmental needs to deal with perceived problems while examining infants, children and adolescents.
Along with a comprehensive plan of care, our medical staff pays special attention to patients which itself dictates the intricacies of our health practices.
Meet the Team
Conditions Treated-
- Pulled/Nursemaid’s Elbow
- Knee Varus/Valgus – Bowed Legs/Knock-Knees
- Flat Foot
- Clubfoot
- DDH (Development Dysplasia of the Hip)
- Deformities
- Obstetrical Brachial Plexus Palsy
- Pediatric Trauma
Services provided -
- Reduction of Pulled Elbow
- Correction of Bow Legs/ Knock Knees
- Club foot Casting (Ponseti Method)
- Reduction of Developmental Dysplasia of Hip (DDH) with Pavlik harness
- All surgeries related to bone injuries
A Glance at the disorders treated –
- Development Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH):
Infants who are in the breech position are more likely to be born with DDH.
It is basically hip looseness or instability coupled with symptoms like legs of different lengths, uneven skin folds on the thigh, less mobility or flexibility on one side, limping, toe walking or a waddling gait.
It can usually be corrected by the use of a harness or brace. If left untreated, it may lead to pain in the hip and the development of wear-and-tear arthritis.
- Clubfoot:
A rare condition called Clubfoot or CTEV (Congenital Talipes Equinovarus), refers to a foot that is turned inwards. It causes the foot to point downwards, ankles and toes turned in, while the feet face each other opposing the normal position. Boys are more likely to be born with clubfoot that girls.
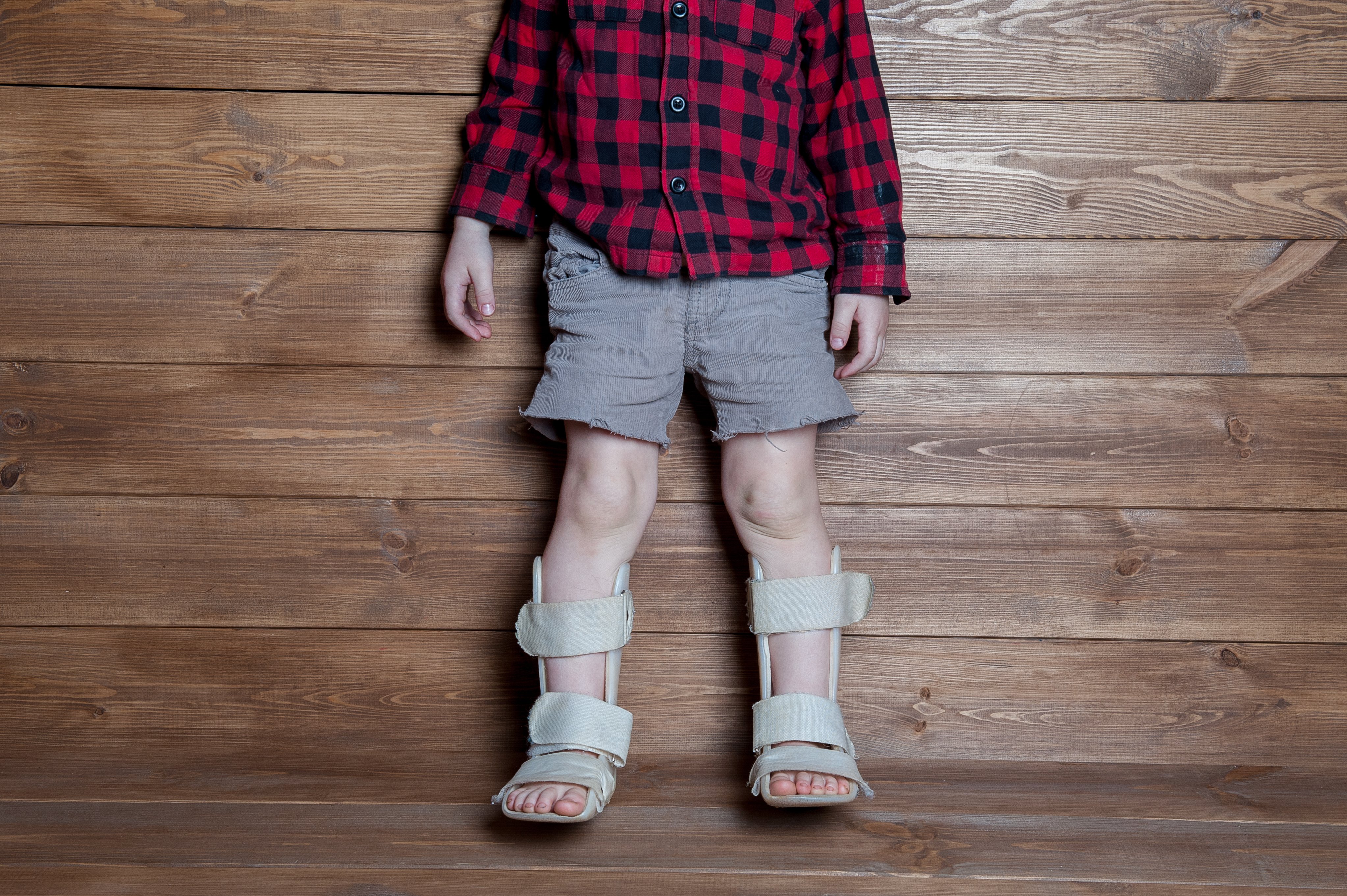
- Bowed Legs/Knock-Knees:
Bowed legs is quite common in infants and toddlers. Bowleggedness is the condition where the knees are wide apart and do not come together while standing.
In most cases, the condition resolves by the age of 3 years. If it is not resolved till then, the child might develop knock-knees (where both the knees come together). Treatment depends on the child’s unique needs and preferences of the parent.
- Pediatric Trauma:
Pediatric Orthopedic surgeons play a vital role in the care of children who may have been injured in an accident or sudden fall. They are trained to recognize and correct even the most minute disruption to the life of a child.
It is important to take professional care and help from them because the sooner your child grows out of the trauma, the more likely they are to develop equally as their peers. They will make sure they answer the questions and doubts in the parents’ minds as well. A pediatric orthopedician would continue to monitor the healing and progress of the child.
- Pulled/Nursemaid’s Elbow:
Nursemaid’s elbow is a common elbow injury in children. It happens when a child’s elbow is pulled and a bone gets dislocated.
Uniquely named, the injury refers to the time when nursemaids or nannies cared for children and had the reputation of causing the injury by pulling on a child’s arm.
Since a child’s elbow is still developing, it takes little force to pull the elbow bones from its place. The child will be reluctant to bend, rotate the elbow or use the arm and will hold the arm still at his/her side.
CTEV – Why Clubfoot Should Be Treated Early
CTEV (Congenital Talipes Equinovarus), more commonly known as clubfoot, is a birth defect where an infant’s foot is twisted inward. The deformity, usually present at birth, worsens over time if left untreated.
A Glance at procedures performed –
- Reduction of Pulled Elbow:
Supination Flexion technique – The pediatric orthopaedic surgeon holds the child’s elbow at 90 degrees with one hand and rapidly supinates the child’s forearm while flexing the elbow with the other hand. The child becomes pain-free and uses the involved limb within minutes post-reduction.
- Correction of Bow Legs/ Knock Knees:
Pathological bow legs and knock knees are corrected by simple surgical procedures either guided growth correction or osteotomy. The procedure to be chosen depends on the skeletal growth remaining. Usually, if more than two years of skeletal growth is left, then we go for guided growth correction in which we stop the growth on one side of the knee temporarily and the deformity gets gradually corrected. On the other hand, if very less or no skeletal growth is left, then we go for osteotomy, that is we break the bone surgically and correct the limb alignment.
- Club foot Casting (Ponseti Method):
We follow the non-surgical method for correction of club foot deformity. In this method, we gradually correct the deformity by multiple serial casting. We change the cast every week and casting is continued till the deformity is almost fully corrected. It usually takes 4 to 6 weeks of casting. Sometimes (if the need is) a small cut is made on the backside of the ankle before the application of a final cast. Once it is fully corrected, the baby is fitted with a brace (special shoes with a bar) for some time.
- Reduction of Developmental Dysplasia of Hip (DDH) with Pavlik Harness:
Once the neonate/infant is diagnosed on ultrasound with DDH, the child is put on a Pavlik harness under supervision in a specified position of hip. The hip is then monitored ultrasonographically multiple times and the position of the harness is changed accordingly till the hip comes back in the desired anatomical position. The Pavlik harness is continued for some time even after the reduction of the dislocated hip to prevent redislocation.
Suggested Readings:
- Jones, S. Khandekar, S.A. (2013) Normal Variants of the Lower Limbs in Paediatric Orthopaedics, International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 4, 2-17 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259240990_Normal_Variants_of_the_Lower_Limbs_in_Pediatric_Orthopedics
- Imrie, M. Scott, V. Stearns, P. & Bastrom, T. (2009) Is Ultrasound Screening for DDH in babies born breech sufficient?, Journal of Children’s Orthopaedics, 4 (1), 3-8 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/38091786_Is_ultrasound_screening_for_DDH_in_babies_born_breech_sufficient
- Agarwal, A. Arkesh, M. & Jandial, G. (March 2018): Sprengel’s deformity correction by vertical scapular osteotomy in a paediatric age group: influence of rib cage abnormalities, International Orthopaedics, 42, 2191-2197 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00264-018-3887-x?shared-article-renderer
- Yamanaka, S. & Goldman, R.D. (June 2018): Pulled elbow in children, Canadian Family Physician 64(6), 439-441 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/325789911_Pulled_elbow_in_children
Tips for Parenting and Child Care
Recent Reviews